In recent years, there has been a growing interest in probiotics and prebiotics due to their potential health benefits, particularly for gut health. While these terms may sound similar, they play different roles in the body and offer distinct advantages. Let’s delve into the world of probiotics vs prebiotics to understand their differences and how they can contribute to your digestive health.
Probiotics: The Good Bacteria
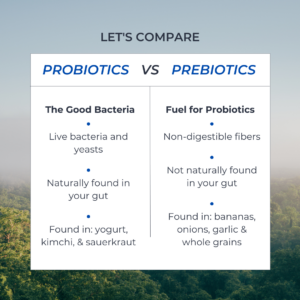
Probiotics are live bacteria and yeasts that are good for your health, especially your digestive system. These beneficial microorganisms can be found in certain foods, such as yogurt, kimchi, sauerkraut, and in supplement form. Probiotics work by helping to maintain a healthy balance of microflora in the gut, which is essential for proper digestion and overall health.
Benefits of probiotics:
- Improved Digestive Health: Probiotics can help regulate digestion, alleviate symptoms of diarrhea, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and other digestive issues.
- Boosted Immune System: A significant portion of the immune system resides in the gut. By maintaining a healthy gut flora, probiotics can enhance immune function and reduce the risk of infections.
- Mood and Mental Health: Emerging research suggests a link between gut health and mental well-being. Probiotics may have a role in supporting mental health and reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Prebiotics: The Fuel for Probiotics
In contrast to probiotics, prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that serve as food for the beneficial bacteria in your gut, including probiotics. Prebiotics can be found in foods like bananas, onions, garlic, and whole grains. By nourishing the good bacteria in your gut, prebiotics help them thrive and improve overall gut health.
The benefits of prebiotics include:
- Improved Gut Health: Prebiotics promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, which can help maintain a healthy gut microbiota and enhance digestive function.
- Regulated Blood Sugar Levels: Some research suggests that prebiotics may help improve insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar levels.
- Weight Management: Prebiotics may also play a role in weight management by promoting feelings of fullness and supporting metabolic health.
The Synergy Between Probiotics and Prebiotics
While probiotics and prebiotics offer unique benefits on their own, they can have a synergistic effect when consumed together. This combination, known as synbiotics, can enhance the survival and activity of probiotics in the gut, leading to improved health outcomes.
In conclusion, both probiotics and prebiotics play crucial roles in promoting gut health, supporting the immune system, and contributing to overall well-being. By incorporating probiotic-rich foods, prebiotic sources, or supplements into your diet, you can help maintain a healthy gut microbiota and potentially experience the benefits of a balanced digestive system.

